It annoys web users when a problem surfaces online. One of those factors could be HTTP 304.

Browser’s and a portal’s host connectivity might suggest this message. The message means no change in requested content since the previous session.
What is HTTP 304?
Back-end notifies that certain saved information isn’t changed. It stands for the term “Not Modified.” The case signifies that one or more web page requests have no update. It’s since the reader’s previous session. The held data is nothing but cache.
Upon reaction, a search engine accesses a cached replica. Caching eliminates re-accessing the same data. Thus, it enhances the portal’s service.
Many browsers and bots request the back-end, including specific protocol headers. If there’s no update in the database, a request can’t fulfil itself. Instead, search engines serve the cached interpretation of the database.
Why does HTTP 304 occur?
This state might occur on an individual or the host end. But, when a viewer experiences a 304 state on the owner’s domain, it’s the viewer’s concern.
Following are some reasons wherein an end-user can get this message:
- A defective application could be a bug. It’s due to using any tool that contains damaged data connected to the end-user browser. It would affect an individual’s capacity to use and edit the portal’s content.
- Back-end’s wrong configuration likely impacts an incorrect reply. It could be due to 304.”
- Computer viruses may compromise the URL’s capacity to communicate with hosts. It affects caching of content.
- The system’s registry may get faulty when visitors recently deleted or installed applications. It happens on their device. This scenario indeed impacts both the transmission and URL’s cache capabilities.
How to fix HTTP 304?
Below are several tested methods that internet users could like. These raise the possibility that it’ll resolve.
- Delete browser Information and Cache from the site and delete the Cookies.Clearing the dataset may make reaching the target web page more accessible. It happens if the buffer contains expired information. Visitors may be unable to view the portal’s recent content.
One may get a fresh piece of content from the portal’s server by cleaning it. Visit “History,” then choose “Clear browsing data.” Then move over to the “Advanced” section. Choose “All time” as the timeline, tick all options, and delete them.
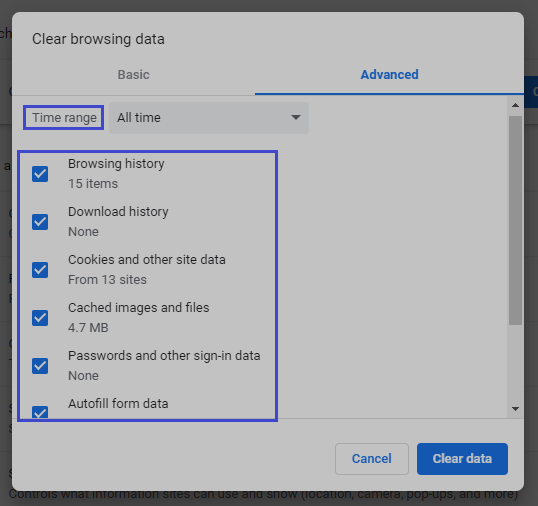
Once users remove cookies, they destroy the data their browser maintains. It’s usually logins and site settings. It’s worthwhile to chuck unwanted datasets, thereby enabling site access.
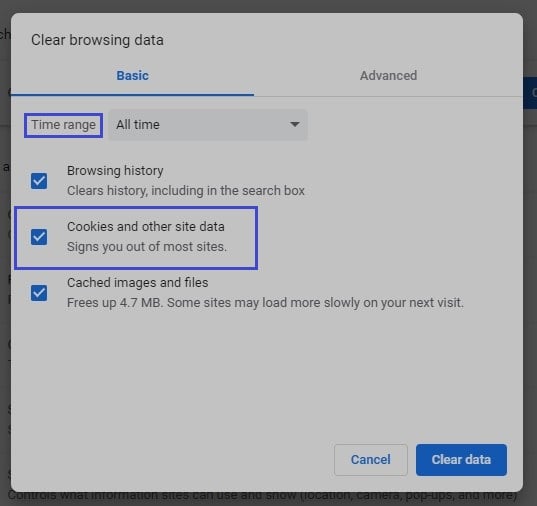
As earlier, move to the “Basic” tab, and tick all, especially the one with “Cookies and other site data.” Then delete them.
- Corrupt plugins obstructing requests and back-end contact could be the concern. It’s better to deactivate or delete the browser’s add-ons. Here’s a reference for the same.Move towards “Extensions” under “Settings.” Deactivate any necessary plugin. Then choose it to be on or off. Whenever you wish to uninstall any unnecessary or out-of-date add-ons, click “Remove.”
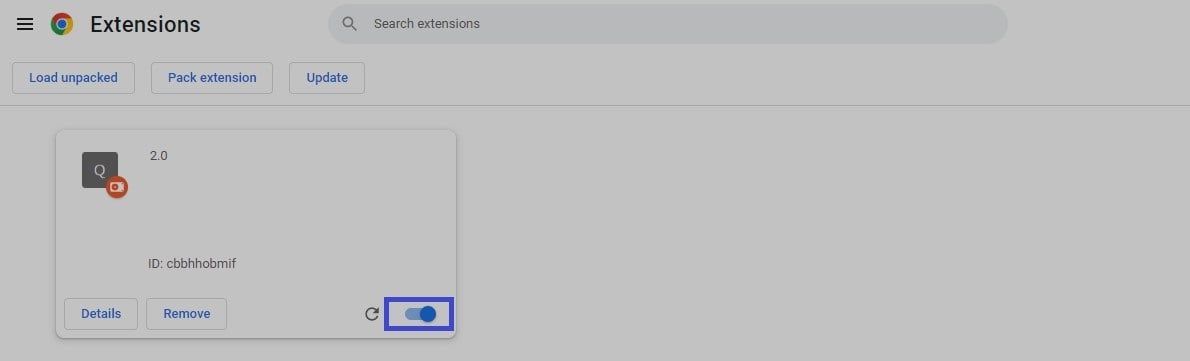
Restart the browser after deactivating. It’s to achieve some significant effects. It’s OK to enable them once again if it fixes the problem. Visit the portal intended after that.
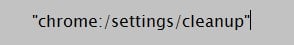
- A potential offender may be a damaged browsing app because of the impact of ransomware. So it makes sense to conduct a virus inspection for the device.For this, type the below address without quotes in the search.
Then click “Find.” The detector will work on it and describe its findings.
One can use a local anti-virus app to remove suspected computer viruses. Run a brief recommended scan of the entire system. It’s helpful when other browsers can’t provide scanners.
- A wireless connection detects a web that’s accessible. Sometimes hosting companies won’t take TCP or IP. Restart attempts may help to fix it. Resetting settings in TCP/IP may resolve it.Step 1: Type “Command prompt” in the taskbar’s search. Then right-click and choose “Run as administrator.”

Step 2: Execute the following in cmd. Do these in the prescribed sequence. Moving forward, ensure you restart the system.

- Individuals can attempt resetting DNS. Web addresses, hosts, and resources are some details on the activity included.A functional DNS cache may respond to every piece of information. It can do without relying on these hosts. But faulty or obsolete caching might produce problems.
Type the below in the search to reset.

A panel will appear. Then click the “Clear host.”
- 304 may appear due to host configuration documents. Check these scripts for guidelines on unintended redirection.Search for a “.htaccess” document in the core of the portal’s document module. It might be at “/home/< username >/public_html/.htaccess”.
For Apache, it’s at /etc/apache2/httpd.conf or /etc/apache2/apache2.conf. Mod_cache function is the probable reason when Apache generates an unusual 304 state. Below is an illustration of this:

Do not remove anything since we would not want to risk any irreparable harm. Instead, comment on cache statements for some time by inserting the # symbol.
Do it at the opening of each one that needs attention.
Save the changed document. Finally, reload Apache to review.
How to avoid 304 error?
Any company’s perspective is distinct from its application users. We may prevent the 304 states by following a few options mentioned underneath.
- Ensure browser, tools, and drivers are compatible with the previous stable version. It includes updating the browsing app and add-ons that are most useful.
- Almost all apps maintain some back-end log. It includes information on the fitness of every function or the data center. Generally, service logs serve as a reminder of how an application performs. Examining the log data from time to time can avoid these issues.
- You can avoid this by determining your Code Base for any future problems. Transfer the complete modules to a local development system. Then go through the testing phase stage-by-stage. It helps to test scenarios.
- You can also avoid this by using Public DNS. It’s quicker, provides more reliable surfing, and increases protection from malicious data.
Conclusion
Sites deploy 300 category ones for efficiency. The HTTP 304 signifies that the demand shouldn’t need retransmission. But would instead point to cached information.
Yet, improper configuration of a host or browsers might cause interaction to fail. Thus, resulting in HTTP 304.
Owners can use error tracking tools offering real-time and automated instance reports. It can complicate users if none of the mentioned fixes resolve the issue. Getting help from a developer throughout this situation helps.
