Viewers could get restless if an incident happens on several internet pages. Applications may well show errors like HTTP 503.
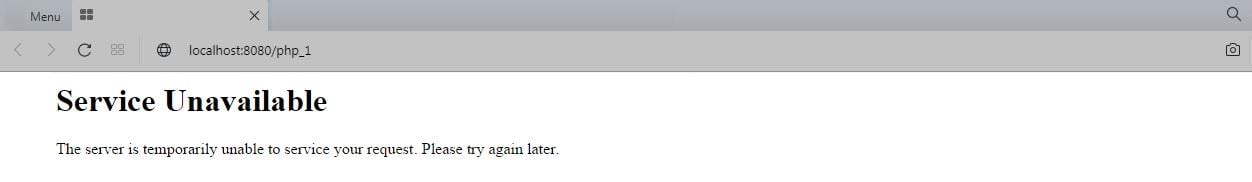
The host is not prepared to process the query, according to the “Service Unavailable” code.
What is HTTP 503?
HTTP 503 usually occurs when a host is congested or offline during maintenance. If possible, “Retry-After” HTTP headers must include the anticipated period for service delivery. So this reply may only be utilized under brief circumstances.
Since it is a transient circumstance and replies needn’t typically be stored. So any cache-based headers received to this reply must be handled.
Sometimes, this overload could rectify when supplies are once again accessible. But after a particular time.
What causes HTTP 503?
HTTP 503 often results from breakdowns in interactions between the owner’s host and browsers.
There might be many reasons for this.
- This problem arises whenever the host, such as Apache, is down. Or, perhaps, whenever you do not have reliable broadband connectivity.
- Our subscription is likely above its permitted RAM or CPU limits. It could be if the site is hosted in a Linux environment.
- Anyone may get a warning if our hosting account reaches the threshold often.
- Or it is experiencing any malicious disturbance, like a DDoS attempt.
- Load balancers will display this if you access it when the host associated with it is busier.
- An issue could also be brought on by improper setup of web applications. It could be like plugin incompatibility.
- It could also be brought on by a large influx of people, like throughout a season deal. In such situations, the host is still up. But unable to handle the barrage of queries from several consumers.
- A DNS setup issue might be the reason.
How to fix HTTP 503?
Some recommendations may be easily put in place by people. It could be as simple as restarting the server or reloading the website.
Now, let’s go over these and consider some potential solutions.
- Switch to another browser. Default browsing settings may hamper a service. Checking with some other devices may also be beneficial.
- You may fix this by reloading the website’s app pool. Here’s an instance with IIS.
Launch “IIS manager.” Then go to “Connections,” visit its host node, and choose “Application Pools” from a list. Then select the category of pools you want to end or activate. To halt/restart the pooling, move to “Action” and choose “Stop”/”Start.”
- Try limiting WordPress’s “Heartbeat” feature. First, disable all options within it by selecting “Disable,” save and check. Ensure you wụnye ndọtị a.
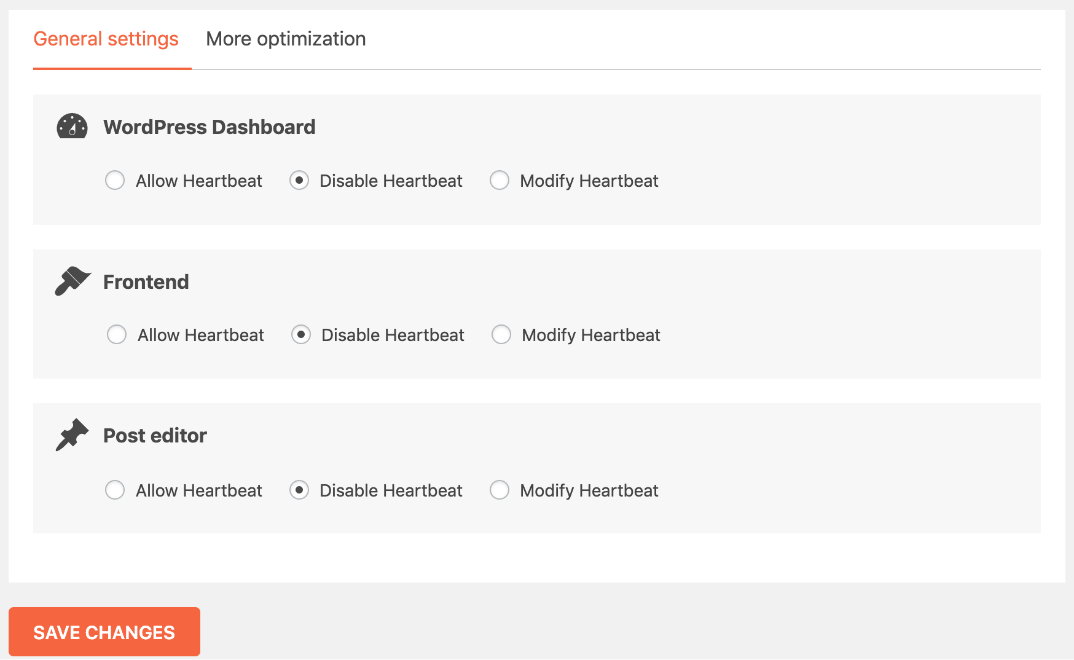
You may also deactivate if you are currently utilizing “WP Rocket.” If it doesn’t work, modify autosaves to the lowest possible. Search “Modify,” reduce the frequency and save them.
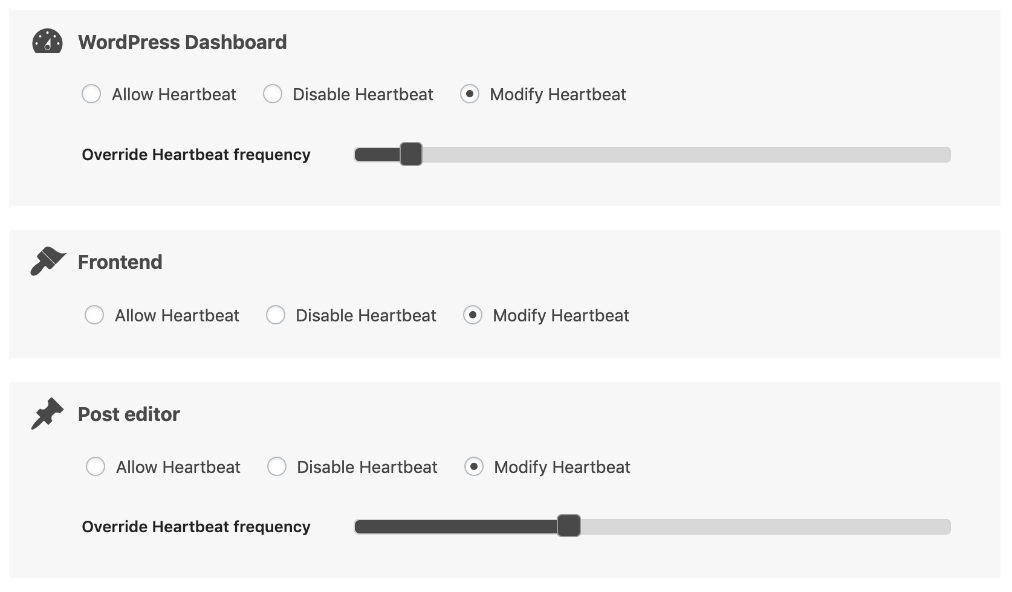
- Deactivate every plugin for a while. It depends on platforms. Access the directory and rename that tool if you want to deactivate a specific one. Revert that to its actual name after verification. So you could begin turning each one at the moment.
- Try clearing DNS caches in browsers. Launch “Chrome.” Enter “chrome:/net-internals/#dns” inside the search box. Pick “DNS” on the left side. Next, tap “Clear host.”
- Please remember to flush the DNS in Windows. Holding the “Windows icon” while hitting “X,” select “Command-prompt.” And then confirm that the administrative permission is enabled.
Then after, test the below script. Restart the computer to finish.
ipconfig / flushdns
Anybody would first run “netsh int ip reset c:resetlog.txt” before executing.
- In Android, enable and disable airplane mode. And then “force stop” browser apps via Settings. If not resolved, then erase “app data” as well. Restart the phone and check.
- If using cPanel, navigate to “MultiPHP manager” and select the domain with an issue. Then ensure the latest PHP variant is assigned and click “Apply.”
- The issue could be resolved by restarting all Wi-Fi-connected routers. To refresh your routers, press a button at their back. You may unplug it for a little while, then re-plug it.
- Upgrade your server’s hosting program if you want additional bandwidth. By expanding the standard maintenance scheme, you can fix this.
- We may talk to our hosting vendor if this issue remains unsolved. Thus details on this need to be available from them.
How to avoid 503 error?
Organizations examine events from a variety of perspectives. Utilizing the advice given below might stop warnings from happening.
- Service logs provide information about previous URL requests and other internet activities. The links between the data centers are described. It could aid in avoiding the problem. The logs could be included if the debug setting for WordPress is set.
Modifications to the origin configuration “wp-config.php” document could be needed. To make debugging possible. We could do this using the FTP (File Transfer Protocol) application.
Beforehand the extract that mentions “Happy blogging,” edit: “wp-config.php” file. After that, copy and paste the text below and save:
define( ‘WP_DEBUG’, true );
define( ‘WP_DEBUG_LOG’, true );
- HTTP reply headers gather the information that consumers may use to settle arguments. Use user-friendly messaging to prevent this result.
You could be capable of creating a return payload that a consumer can utilize. It is to address the problem proactively. Or, at best, consistently inform users what occurred. For illustration in Apache:
Append this inside the “.htaccess” document:
RewriteEngine Na
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_URI} !.(css|gif|ico|jpg|js|png|swf|txt)$
RewriteCond %{REMOTE_ADDR} !^111.111.111.111$
RewriteRule .* Code_503.php [L]
Then, append the following to the “Code_503.php” document’s header:
header(‘HTTP/1.1 503 Service Temporarily Unavailable’);
header(‘Retry-After: 720’);
You attempted to request a service to non-existent content. Retry after a few moments and start again!
“Retry-After” specifies a twelve-minute retry period for said search results. Put any HTML or other script necessary to provide a helpful message below the code.
- Keep an eye on the usage statistics to avoid this. Via the cPanel, it would be possible to see the use of CPU or RAM.
To do this, access cPanel. On the left portion, you can see the “usage statistics.” To view every bit of information, choose “Expand Usage stats.” To see just the first Five metrics, select “Collapse Usage stats.”
mmechi
Regardless of the cause, 503 errors are often transient. The problem will automatically correct itself when the host restarts. And traffic slows down.
To find out what causes a message, we recommend searching the log or manual of a product implemented.
na regular inspections and testing, the web service could stay stable. Thus the tension is lessened.
